Space figures
Cross-section
Volume
Surface area
Cube
Cylinder
Sphere
Cone
Pyramid
Tetrahedron
Prism
|
|
|
|
A space figure or three-dimensional figure is a figure that has depth in addition to width and height. Everyday objects such as a tennis ball, a box, a bicycle, and a redwood tree are all examples of space figures. Some common simple space figures include cubes, spheres, cylinders, prisms, cones, and pyramids. A space figure having all flat faces is called a polyhedron. A cube and a pyramid are both polyhedrons; a sphere, cylinder, and cone are not.
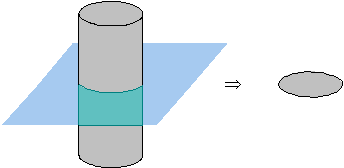
A cross-section of a space figure is the shape of a particular two-dimensional "slice" of a space figure.
Example:
The circle on the right is a cross-section of the cylinder on the left.
The triangle on the right is a cross-section of the cube on the left.

Volume is a measure of how much space a space figure takes up. Volume is used to measure a space figure just as area is used to measure a plane figure. The volume of a cube is the cube of the length of one of its sides. The volume of a box is the product of its length, width, and height.
Example:
What is the volume of a cube with side-length 6 cm?
The volume of a cube is the cube of its side-length, which is 63 = 216
cubic cm.
Example:
What is the volume of a box whose length is 4cm, width is 5 cm, and height is
6 cm?
The volume of a box is the product of its length, width, and height, which is 4 × 5 × 6 = 120
cubic cm.
The surface area of a space figure is the total area of all the faces of the figure.
Example:

What is the surface area of a box whose length is 8, width is 3, and height is 4? This box has 6 faces: two rectangular faces are 8 by 4, two rectangular faces are 4 by 3, and two rectangular faces are 8 by 3. Adding the areas of all these faces, we get the surface area of the box:
8 × 4 + 8 × 4 + 4 × 3 + 4 × 3 + 8 × 3 + 8 × 3 =
32 + 32 + 12 + 12 +24 + 24=
136.
A cube is a three-dimensional figure having six matching square sides. If L is the length of one of its sides, the volume of the cube is L3 = L × L × L. A cube has six square-shaped sides. The surface area of a cube is six times the area of one of these sides.
Example:
The space figure pictured below is a cube. The grayed lines are edges hidden from view.

Example:
What is the volume and surface are of a cube having a side-length of 2.1 cm?
Its volume would be 2.1 × 2.1 × 2.1 = 9.261
cubic centimeters.
Its surface area would be 6 × 2.1 × 2.1 = 26.46
square centimeters.
A cylinder is a space figure having two congruent circular bases that are parallel. If L is the length of a cylinder, and r is the radius of one of the bases of a cylinder, then the volume of the cylinder is L × pi × r2, and the surface area is 2 × r × pi × L + 2 × pi × r2.
Example:
The figure pictured below is a cylinder. The grayed lines are edges hidden from view.
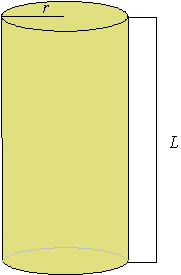
A sphere is a space figure having all of its points the same distance from its
center. The distance from the center to the surface of the sphere is called its
radius. Any cross-section of a sphere is a circle.
If r is the radius of a sphere, the volume V of the sphere is given
by the formula V = 4/3 × pi ×r3.
The surface area S of the sphere is given by the formula S = 4 × pi ×r2.
Example:
The space figure pictured below is a sphere.

Example:
To the nearest tenth, what is the volume and surface area of a sphere having a
radius of 4cm?
Using an estimate of 3.14 for pi,
the volume would be 4/3 × 3.14 × 43 = 4/3 × 3.14 × 4 × 4 × 4 = 268
cubic centimeters.
Using an estimate of 3.14 for pi, the surface area would be 4 × 3.14 × 42 = 4 × 3.14 × 4 × 4 = 201
square centimeters.
A cone is a space figure having a circular base and a single vertex.
If r is the radius of the circular base, and h is the height of the
cone, then the volume of the cone is 1/3 × pi × r2 × h.
Example:
What is the volume in cubic cm of a cone whose base has a radius of 3 cm, and
whose height is 6 cm, to the nearest tenth?
We will use an estimate of 3.14 for pi.
The volume is 1/3 × pi × 32 × 6 = pi ×18 = 56.52,
which equals 56.5 cubic cm when rounded to the nearest tenth.
Example:
The pictures below are two different views of a cone.


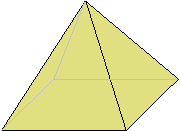
A pyramid is a space figure with a square base and 4 triangle-shaped sides.
Example:
The picture below is a pyramid. The grayed lines are edges hidden from view.
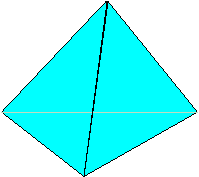
A tetrahedron is a 4-sided space figure. Each face of a tetrahedron is a triangle.
Example:
The picture below is a tetrahedron. The grayed lines are edges hidden from view.
A prism is a space figure with two congruent, parallel bases that are polygons.
Examples:
The figure below is a pentagonal prism (the bases are pentagons). The grayed lines are edges hidden from view.
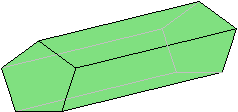
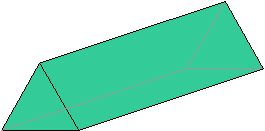
The figure below is a triangular prism (the bases are triangles). The grayed lines are edges hidden from view.
The figure below is a hexagonal prism (the bases are hexagons). The grayed lines are edges hidden from view..

![]()
![]() Visit the Math League
Visit the Math League
![]()